Planned Land Use Checker
General Microservice Description
The purpose of this service is to automate the compliance checks of land use regulations applicable to buildings in Germany. It can be used in scenarios where land use regulations are specified in the XPlanung format, and building designs are stored in formats convertible to CityGML 2.0 or 3.0 regarding their spatial design and specification of uses of spaces. An example of such a format is IFC, also commonly used in Germany for Building Information Modelling.
XPlanung is an open, XML-based data exchange format based on Geography Markup Language Version 3 (GML 3.2.2), the extensible standard for spatial data developed by the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) and ISO TC211. The CityGML standard defines a conceptual model and exchange format for the representation, storage and exchange of virtual 3D city models. The standard provides a framework for integrating, storing, and exchanging 3D geospatial data encoded in GML/XML.
Transformation of BIM data in IFC format into CityGML 2.0 is implemented as a custom FME workflow.
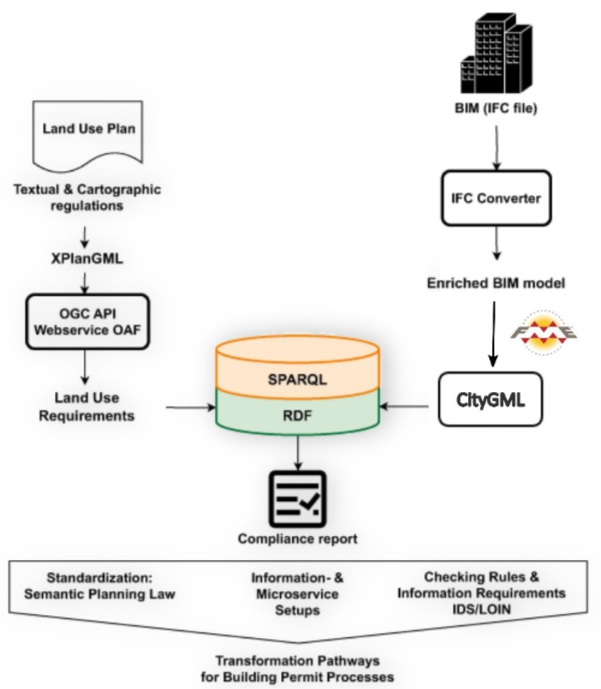
GraphDB as the storage for land use data and BIM data
Graphwise GraphDB(TM) is used as the storage for German use case 1 data, namely, land use development plans of the land under Tegel airport and building information models of several buildings of Tegel airport. The description of the use case is provided in the Section 5.1 of the ACCORD Deliverable D1.2.
Land use development plans are given in the form of XPlanGML files, and to be uploaded and then queried in Graphwise GraphDB(TM) they undergone conversion from XPlanGML into RDF/Turtle done with custom script written in XSPARQL.
Building information models (BIMs) are given in the form of IFCx4 files, and to be uploaded and then queried in Graphwise GraphDB(TM) they are converted from IFCx4 to CityGML 3.0 with the help of a custom FME workflow, and then converted from CityGML 3.0 into RDF/Turtle with another custom script written in XSPARQL.
Important note: the geometries in XPlanGML are given originally in GML format, and to be used within Graphwise GraphDB(TM) they are converted into WKT using custom Python code.
The data of land usage plans are stored in GraphDB repositories 12-50a, 12-50ba and 12-62a, corresponding to the names of building plans.
Each repository contains (here links are given for the repository 12-50ba):
the unnamed default graph- stores common SKOS concept schemas for enumerations and code values reused within XPlanGML;landuse- land use data from XPlanGML for the particular building plan;ifc- conversion of building information models (BIMs) of Tegel airport from IFCx4 to CityGML 3.0 with FME conversion and then XSPARQL conversion to RDF;ifc/heights- extracted heights of BIM model components2dfp- BIM 2d footprint in RDF;2d- precalculated areas of intersection of BIM 2d footprint elements with land parcels;toporels- precalculated topological relations between land parcels and BIMsregurels- interconnections among fragments of texts detected in regulations texts, that cannot be described in XPlan;topoenv- precalculated topological relations between land parcel envelopes
The documentation and the details of German use case are given in https://github.com/Accord-Project/Tegel/tree/main (private).
Reusable scripts and GME workflows are given in the public Github repository https://github.com/Accord-Project/Tegel-scripts.
Microservice Implementation and Functionality
This service transforms XPlanung and CityGML models into RDF graphs and topology relations between their geometries are materialised using predicates of the GeoSPARQL ontology. Materialised topological relations are equivalent to outputs of GeoSPARQL topological functions with sets of 2D and 3D geometries transformed from XPlanung and CityGML provided as arguments. Materialisation of topology relations between geometries in both models serves as a link between two models in one RDF graph, making both models semantically interoperable, as shown below:
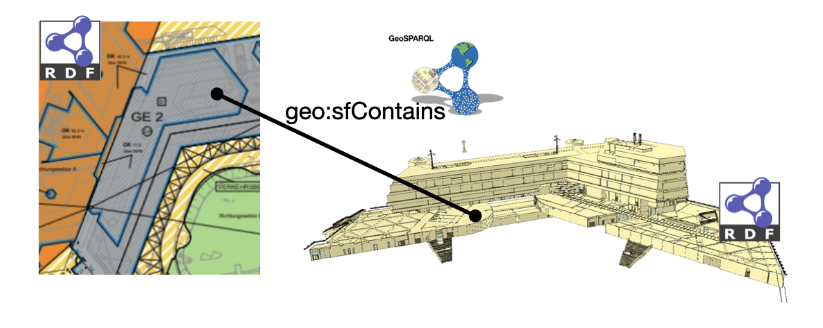
SPARQL enables querying information from databases or any data source that can be mapped to RDF. The SPARQL standard is designed and endorsed by the W3C and helps users and developers focus on what they would like to know instead of how a database is organised. This service makes use of those capabilities of the query language to retrieve geometries of parts of a building that are topologically related to land parcels’ geometries, and check using more semantically rich descriptions of such building geometries whether the building complies with the requirements of the XPlanung.
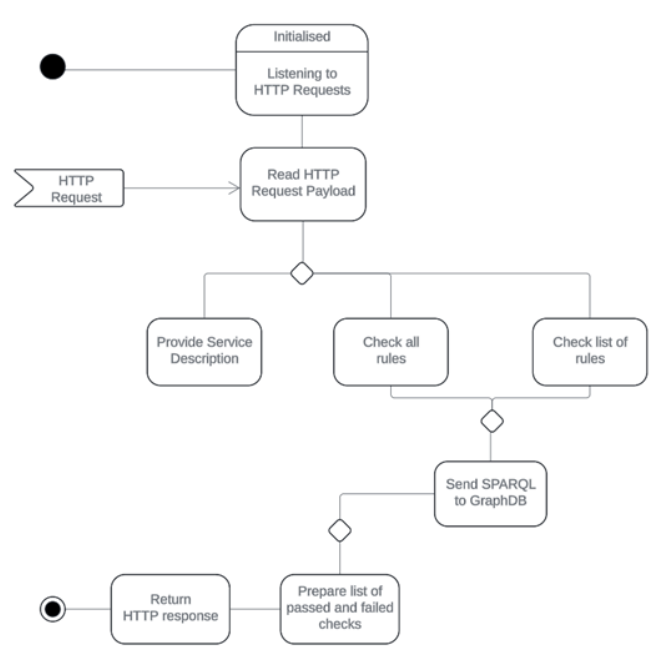
The service is implemented in Java using Spring Boot framework. The information flow, illustrated in the activity diagram, is as follows:
-
Upon initialisation, the service listens to HTTP Post requests.
-
Upon receiving a service description request, it returns a description of its functionality and the numbered list of implemented rules it is capable of checking in HTTP response.
-
Upon receiving the request to check all rules, it sends SPARQL queries, corresponding to every implemented check, to GraphDB and returns a list of passed and failed checks when all queries are finished, in HTTP response.
-
Upon receiving the request to check one or more specific rules, it sends SPARQL queries, corresponding to each check from the list, to GraphDB and returns a list of passed and failed checks when all queries are finished, in HTTP response.