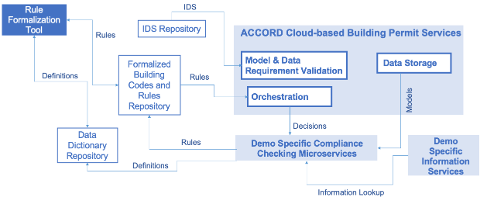
Extensibility of ACCORD Cloud Architecture
Extensibility of the ACCORD framework is achieved via two methods: (1) Customisation of Permitting Process and (2) Addition of the new Microservices.
Customisation of Permitting Process: The ACCORD process execution component provides the ability to execute a custom permitting process. The ACCORD project proposes a default process (described in Section 3.7), but the intention is for each user of the ACCORD framework to specify their own process. This allows each permitting authority to customize their process and the ways in which ACCORD components are composed to perform their own permitting process.
Addition of new Microservices: As new digitised regulations are added to the ACCORD system, new microservices can also be added to support their execution. The process of adding new microservices consists of the following generic steps:
- Determine if a new microservice is needed: Firstly, it should be verified that a new microservice is indeed necessary and that no existing microservice already supports the functionality being implemented.
- Analyse required BCRL Terms: The BCRL terms identified via the ACCORD rule formalization process should be analysed, and the implementation of the microservice should be aligned with this so that each individual functional check to be implemented within the microservice aligns with each BCRL term. An example of this is shown in the figure below.
- Select checking method: Once the functional checks have been defined their implementation method should be defined. This could include (a) manual implementation, (b) use of external software tool, (c) use of external component via API.
- Implement checking method: The final checking method should be implemented/integrated.
- Implement Data API: To access model data (either IFC or GIS) the microservice should utilise the Data API to retrieve it from the core ACCORD data storage service.
- Implement Results API: Once the implementation is complete it should be exposed to the other ACCORD components via the implementation of the results API.
- Register Microservice in Data Dictionary: Finally, the microservice should be registered in the data dictionary and associated with appropriate BCRL terms to enable it to be utilised by the core ACCORD components.